Please email eric@www.colorsynth.com if you wish to discuss custom kit options.
ColorSynth Standard DIY Kit – $99 + shipping and tax (where applicable)
Note: The following items are not included with the Standard DIY kit:
-8″ Globe
-Black ABS enclosure/fixture
-Standoffs, screws and mounting hardware
-Power on/off switch
-Cables/wiring
-Cable headers for PCB
Standard DIY kit part list:
|
Index
|
Description |
Value
|
QTY
|
Notes |
|
IC1
|
16F1827I/P Microprocessor |
1
|
Loaded with ColorSynth firmware v2010-12-30 | |
| 18P IC socket for IC1 |
1
|
|||
|
IC2
|
PC900V optocoupler |
1
|
For MIDI RX | |
|
VREG1
|
LM7808 +8VDC regulator, 1A |
1
|
For use with LED included in this kit | |
|
VREG2
|
78L05 +5VDC regulator, 100mA |
1
|
For microcontroller and POTs | |
|
Q1
|
Crystal |
12Mhz
|
1
|
|
|
SW1
|
6 Position DIP switch, right angle |
1
|
Assigns MIDI channels, power TX, and Knob/local control | |
|
C1
|
Capacitor |
1uF
|
1
|
Power smoothing |
|
C2
|
Capacitor |
.1uF
|
1
|
Power smoothing |
|
C3
|
Capacitor |
.01uF
|
1
|
Power smoothing |
|
C4, C5
|
Capacitor |
22pF
|
2
|
For crystal |
|
D1
|
1n4001 protection diode |
1
|
For mismatched PSU polarity | |
|
D2
|
1n914b diode |
1
|
For MIDI RX | |
|
R1-R3
|
1W resistor 1% |
10
|
3
|
For LED driving circuit |
|
R4
|
1/4W resistor 1% |
3.6k
|
1
|
RA3 to base of RED transistor |
|
R5, R6
|
1/4W resistor 1% |
4.7k
|
2
|
RA4 to base of GREEN transistor, RB3 to base of BLU transistor |
|
R7, R9, R10
|
1/4W resistor 5% |
220
|
3
|
MIDI RX and TX |
|
R8
|
1/4W resistor 5% |
280
|
1
|
MIDI RX |
|
R11-R16
|
1/8W resistor, 5% |
10k
|
6
|
Dip switches, pushbutton |
|
T1-T3
|
BC337 NPN transistor |
3
|
Transistors for RGB LED driving circuit | |
|
LED
|
Common Anode 3W RGB LED |
1
|
Driver circuit daws ~120mA current for red, green, and blue LEDs. The voltage drop for each LED color can range from 1-5V. | |
|
HEATSINK
|
Heatsinks for LM7808 and LED |
2
|
||
|
POT1-3
|
Panel mount linear potentiometer |
10k
|
3
|
Datasheet |
|
KNOB1-3
|
Knobs for POT1-3 |
3
|
Datasheet | |
|
SW2
|
Pushbotton switch |
1
|
Datasheet | |
|
MIDI 1,2
|
5 pin DIN connector, panel mount |
2
|
Datasheet | |
|
DC JACK
|
DC power jack 2.5mm x 5mm |
1
|
Datasheet | |
|
PSU
|
Power Supply |
1
|
For US 110V AC power, converts to 12VDC+, 1A current, 2.5mm | |
|
PCB
|
ColorSynth PCB v1.0 |
1
|
Note 1) LED driver circuit assembled in breadboard portion of PCB | |
|
Note 2) PCB originally designed for 16F88 microcontroller, 16F1827 will need RA3, RA4, RB0 and RB1 to be hand wired to PCB |
Assembly Instructions:

Take inventory of all the parts.
–Hi-Res pic of all parts
–Closer view #1
–Closer view #2
–Closer view #3
–Closer view #4
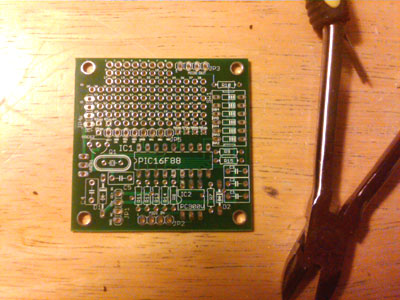
Start with the PCB in this orientation.
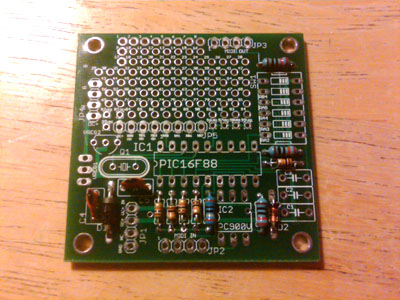
Insert and solder the MIDI and dip switch resistors, as well as the diodes and crystal capacitors.
1) C4-C5 (22pF)
2) R8 (280 ohms: red, grey, black, black)
3) R7, R9-R10 (220 ohms: red, red, black, black)
4) D1 (1n4001: polarized, should match the orientation of the grey stripe in the picture)
5) D2 (1n914B: polarized, should match the orientation of the black stripe in the picture)
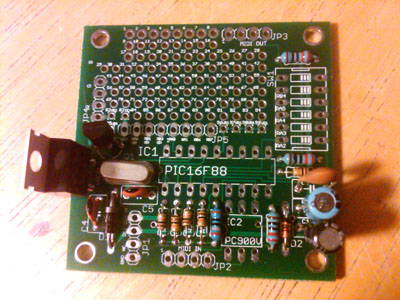
Add the crystal, voltage regulators and power caps.
1) VREG1 (LM7508, orientation should match picture)
2) VREG2 (78L05, orientation should match picture)
3) Q1 (12Mhz crystal)
4) C3 (.01uF, ceramic cap pictured, non polarized)
5) C2 (.1uF, polarized, negative lead is marked and should be on the right hand side as pictured)
6) C1 (1uF, polarized, negative lead is marked and should be on the right hand side as pictured)

Add the socket, dip switch, and optocoupler. You might choose to add your own headers like in this picture.
1) DIP18 (goes where IC1 goes, notch is on the left as pictured)
2) SW1
3) IC2 (PC900V, white dot should be positioned in the lower left near JP2)
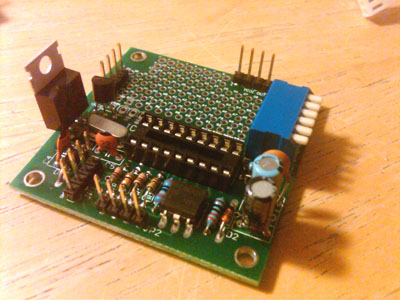
Alternate view.

1) Attach the heatsink to the LM7808 regulator, use a thermal compound and a 4-40 screw with nut.
2) Insert the 16F1827 microprocessor (datasheet) with the notch closest to the crystal and LM7808 regulator, it should match the orientation of the DIP18 socket. (The 16F88 is pictured, the Standard DIY kit comes with a 16F1827 that has four pins clipped and tinned with solder. When installing the microprocessor, those tinned pins should be on the side of the socket that is closest to the PC900V and the 10k resistors.)
Mainboard jumper/pin connections
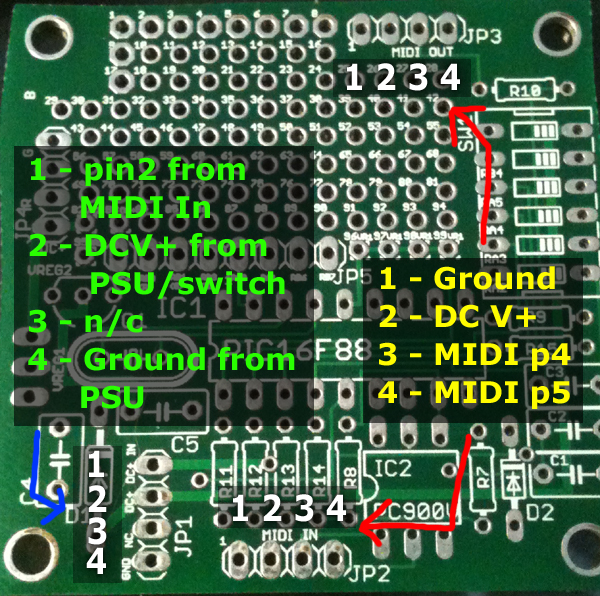
JP1 is the power connector:
Pin1) This is connected to Pin2 of JP2 which is DC+ from power over MIDI.
Pin2) This is the DC+ input to the board, 12 to 15V is ideal.
Pin3) Is not connected
Pin4) Is ground
-If you only want to use power over MIDI, wire pins 1 and 2 together.
-If you only want to use a wall wart power supply, wire the positive terminal of your power jack to pin 2 and the ground terminal to pin 4.
-If you want to use a switch between a wall wart and power over MIDI, wire the negative terminal of your power jack to pin 4, the positive terminal to one side of your switch, pin 1 of JP1 to the other side, and pin 2 to the center of your switch.
JP2 and JP3 are MIDI in and out:
Pin 1) Ground for power over MIDI (MIDI pin 1)
Pin 2) DC+V for power over MIDI (MIDI pin 3) (on JP3 this is switched on/off by pin 6 of the dipswitch)
Pin 3) MIDI pin 4 (data).
Pin 4) MIDI pin 5 (data).
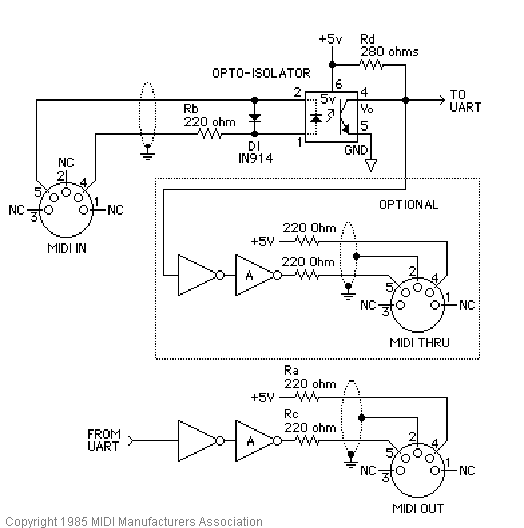
This is the MIDI electrical specification if you need clarification on which MIDI pins this refers to.
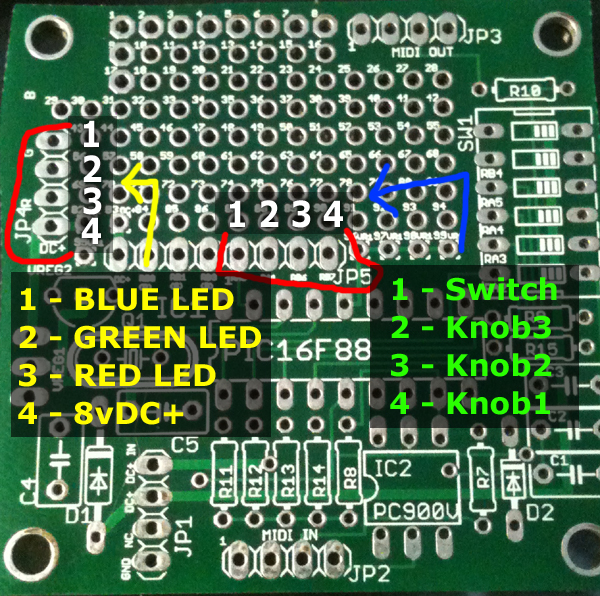
JP4 is the LED connector:
Pin 1) Blue LED cathode (-)
Pin 2) Green LED cathode (-)
Pin 3) Red LED cathode (-)
Pin 4) Common anode for all (+). Fed 8vDC+ from LM7808 on the mainboard.
JP5 is the external switch/knobs connector:
Pin 1) External switch (alternates what the knobs do, 3 banks described below)
Pin 2) Knob 3 (Master level, blue osc, blue level)
Pin 3) Knob 2 (Strobing, green osc, green level)
Pin 4) Knob 1 (Color Osc, red osc, red level)
Note: A new version of the PCB is being designed that will make the following steps easier and/or unnecessary in future versions of the DIY KIT.
Assembly of the LED driver circuit:
The ColorSynth PCB V1.0 was designed to be used to make ColorSynths, but is also designed for use with other custom MIDI devices. To help facilitate this, a small breadboard area was added to the PCB. The LED driver circuit of the ColorSynth is installed into this breadboard.
Here is the schematic of the circuit:
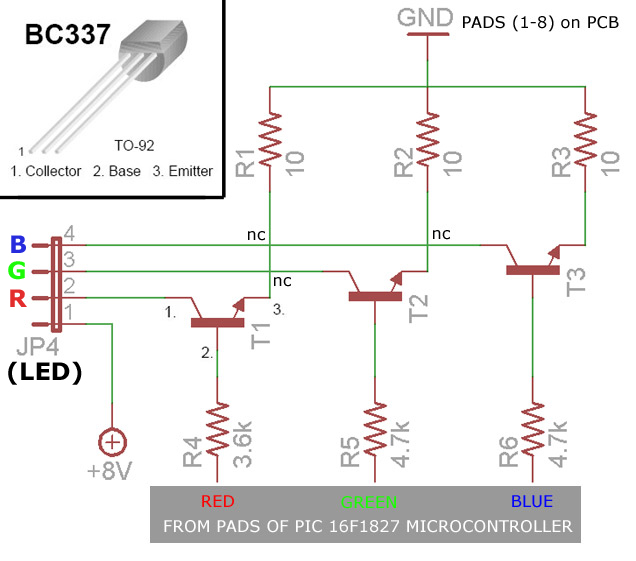
(For those unfamilliar with reading circuits, the green lines when crossed do not form an electrical connection with each other. I’ve marked these junctions “NC”, or no connection, for clarity).
First place the transistors into the breadboard, evenly spaced apart. Reference the animated gif below for an idea on positioning. Then follow the instructions to wire the circuit.
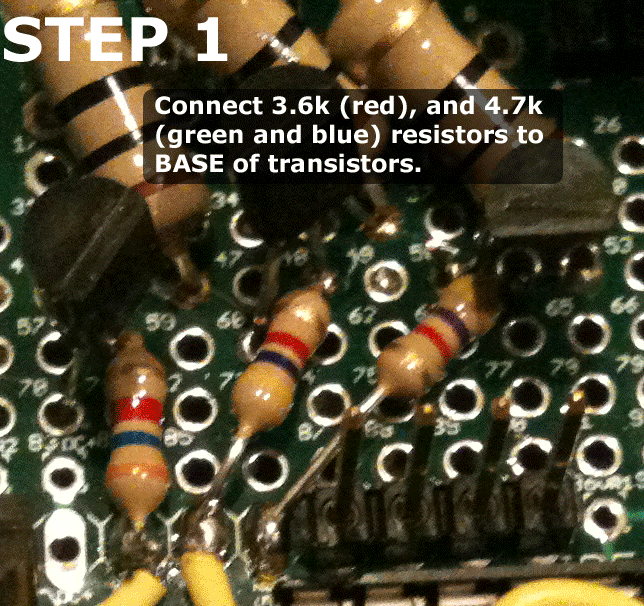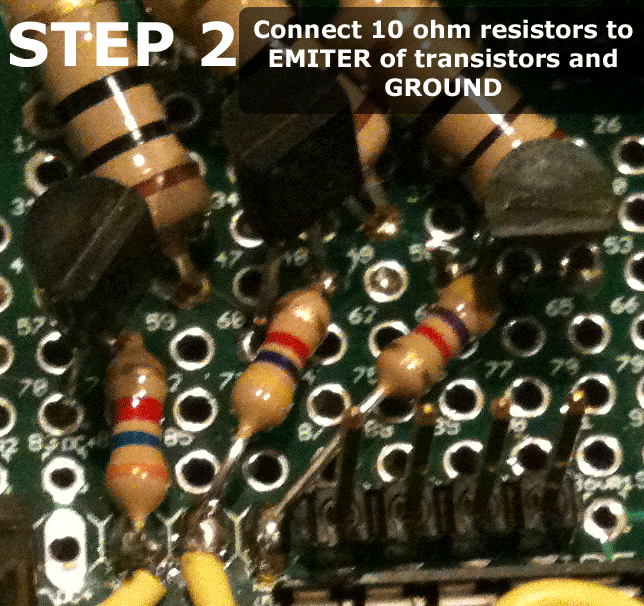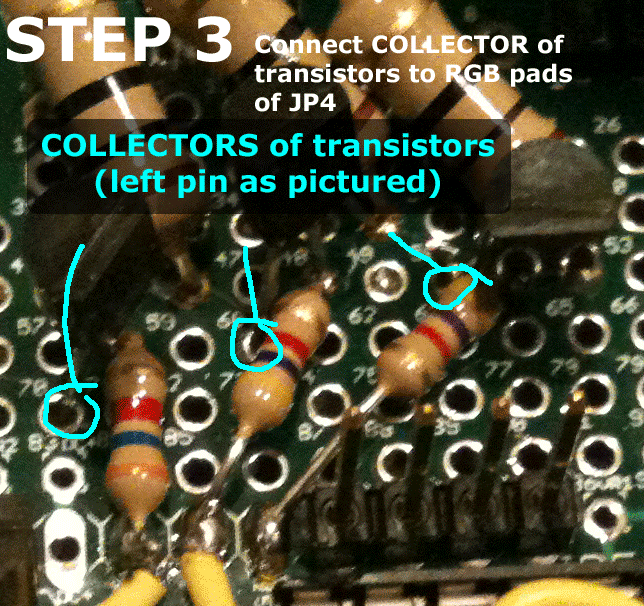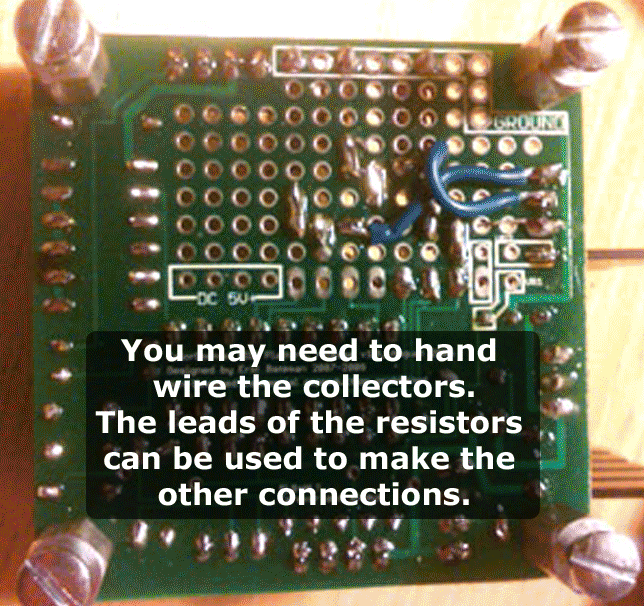
Please email eric@www.colorsynth.com if you have any questions.
Wiring the 16F1827 to the PCB

(naked PCB with 16F1827 shown without 18P socket for visual clarity)
The PCB was originally designed for a 16F88. Revisions have been made to the ColorSynth firmware that have drastically improved performance, but require a 16F1827 (datasheet) which has a different pinout than the 16F88. A new PCB design is forthcoming, for now you will need to hand wire these four pins to the PCB as pictured above:
1) RED – wire pin2 (RA3) to the (R) pad above the IC1 text and to the right of the pad labeled “DC+”.
2) GREEN – wire pin3 (RA4) to the (G) pad next to the (R) pad
3) BLUE – wire pin6 (RB0) to the lead of R12 that is closest to the microcontroller
4) YELLOW – wire pin7 (RB1) to the lead of R13 that is closest to the microcontroller
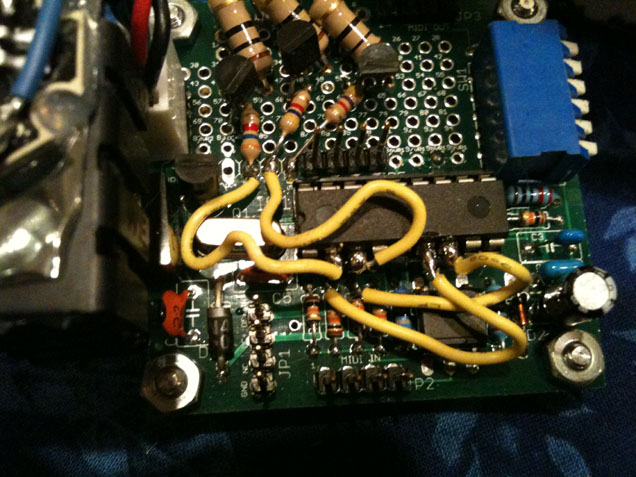

When you are done it should look like this.
Wiring the potentiometers and switch
The external pots and pushbutton allow you to control the ColorSynth without a MIDI controller. The pots and switch are connected to the pads of JP5:
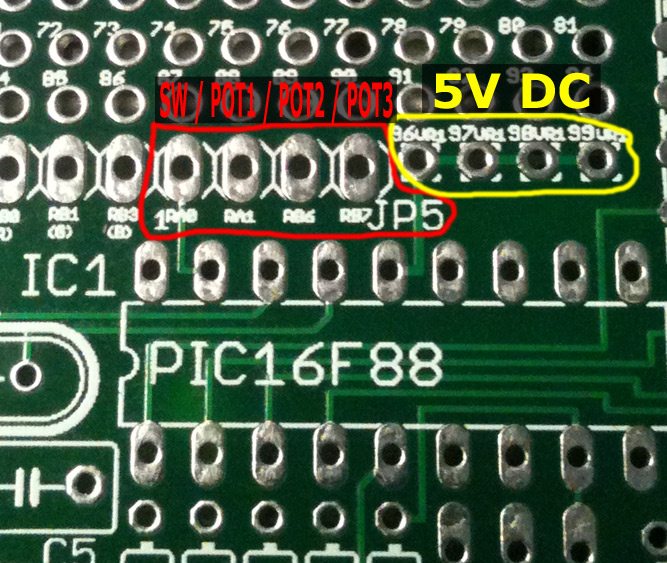
If you don’t wish to use the pots/switch, you can solder them to ground.
This schematic shows how to wire the pots and switch:
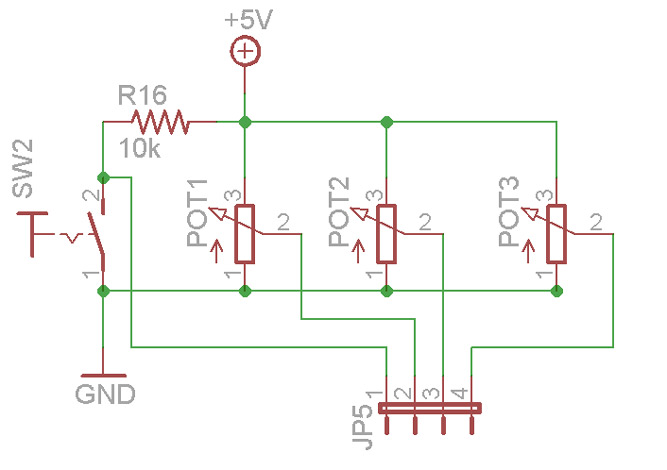
(the green dots indicate areas where the crossed wires/signals make an electrical connection)
1) Wire one side of each pot to ground (pads 1-8 on the PCB breadboard) and the other side of each pot to the 5V pads indicated in the picture above.
2) Wire the slider/wiper of each pot to it’s corresponding pad of JP5.
3) Solder one lead of R16 (10k 1/8w) to one terminal of the pushbutton.
4) Solder the other lead of R16 to the 5V supply. If the pushbutton is close enough to the pots you can solder it directly to one of the 5V sides of any of them.
5) Wire the other terminal of the pushbutton to ground (again you can use the pots).
6) Wire the 10k terminal of the pushbutton to PAD1 of JP5 as indicated above.